For several years in a row, the blockchain community and even beyond have been talking a lot about NFTs. They were created, bought, sold, given as gifts - and continue to be used to this day, although perhaps not so openly.

Next, let's talk about what the market of non-fungible tokens represents, what technical features characterize them, and how entire collections are created.
What is an NFT?
NFT (Non-Fungible Token) is a unique digital asset in the blockchain ecosystem. Like cryptocurrency, it is also a record in a decentralized distributed ledger, but the nature and functions of NFTs differ from regular payment tokens. Cryptocurrencies can be compared to traditional currencies. There are several million Bitcoins in the world: they have sufficient value, a high price, and a limited quantity. But two bitcoins are indistinguishable from each other: they are equivalent coins that can be exchanged for each other without losing or gaining anything in the process.
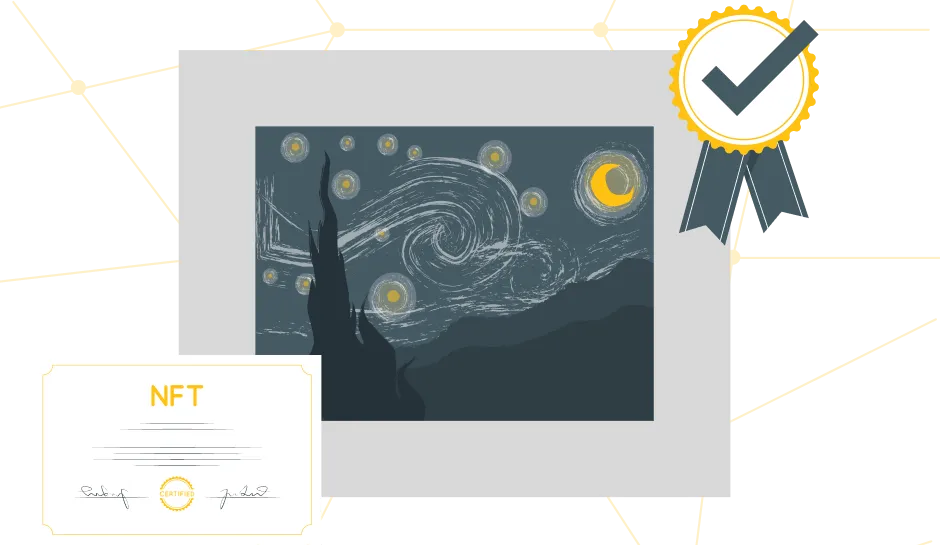

NFTs are unique units assigned a special value, a digital identifier that helps distinguish them from others. Each non-fungible token has its own value and differs from another. Even if two NFTs are sold at the same market price, their exchange will not be equivalent in terms of the blockchain. Furthermore, NFT automatically attaches ownership rights to its owner, and in the future, this right can be tracked and confirmed through the infrastructure of the distributed ledger. Such a feature will eventually allow applying non-fungible tokens in niches where transaction transparency is critically important.
What NFTs Are Used For
The unique nature of NFTs has determined the main scenarios for their use - for example, in the field of collecting, art, and entertainment.

Collecting
The first boom in the NFT market was associated precisely with collecting and works of art. Digital artists tokenized their works and sold them at auctions - sometimes for very large sums of money. Some paintings were auctioned off for millions and tens of millions of dollars.
From the collector-buyers` perspective, this was an investment in rare and unique assets, the price of which on the market could potentially increase even further.
Blockchain Games
NFTs are also used in blockchain games as a form of authentic, scarce digital property. Thanks to distributed ledger technology, NFTs give players access to several opportunities:

- Unique in-game items. Everything is the same as in regular games: skins, weapons, accessories, pets, which are purchased for collection or for advantages during gameplay. But with NFTs, the ownership of these items is not just verbal; it is recorded in the blockchain.
- Trading on internal and external markets. NFTs contribute to the creation of an in-game economy: they can be exchanged, as well as sold and bought - both in the game itself and at auctions outside it.
- Monetization. Thanks to NFTs, earning in games has become more real: rare and in-demand items can drop to the player for free during the game and then be sold for real money. This practice is also found in traditional games, but some providers prohibit it and may even block the account.
- Creating your own content. This feature is not available in all blockchain games, but where it is provided by the developer, the user can create their own skins, accessories, and items and tokenize them, turning them into NFTs.
Of course, not only players earn in such games — creators also do not stand aside. They profit from investments even during the development process and then monetize the game by selling tokens, transaction fees with them, and other in-game processes.
Metaverses
The Internet generation of Web 3.0 has set a trend for metaverses - digital virtual worlds where you can do anything. It is NFTs that become the main functional tool in them.
To use metaverses, the user creates an NFT of their digital avatar. Inside the virtual world, he can buy other tokens:

- Clothes, shoes, and accessories for his avatar
- Land plots
- Real estate, and more
Transparent market economy in virtual worlds is another merit of non-fungible tokens. For now, metaverses are mainly used by individuals and some commercial projects, but if the trend develops, theoretically, other players may join in — more brands, more financial institutions, and even government institutions. In that case, the transparency and traceability of assets will be very handy.

There are already examples of such ecosystems in the market — for example, Decentraland, where land plots act as non-fungible tokens. They can be bought, sold, and developed at the discretion of the owner. The project has become so popular that even Samsung and the Domino's pizza chain have opened their stores in this metaverse, and the price of some plots has exceeded $1 million.
A Brief History of the NFT Market
The first NFT projects appeared on the market as early as 2012, but for the next 5 years, few knew about this technology and even fewer used it. The peak of popularity of this sector came during 2017-2021 and began with the first major and truly famous collection — Crypto Punks.

It was created by Larva Labs, a studio developing digital games and software, and released to the market in June 2017. The collection consists of 10,000 unique pixel characters, each of which represents a non-fungible token on the Ethereum blockchain. Each character has a distinguishing feature: an accessory, skin color, or hairstyle - these determine its rarity and value. Interestingly, during development, these 10,000 NFTs were generated randomly using procedural generation algorithms — absolutely without any intervention from artists.
Upon completion of development, Larva Labs offered its NFTs for free to anyone who wanted them → the giveaway lasted only a few days. After that, the punks began to be sold. Over time, some crypto punks became so sought after that some of them were valued in the millions of dollars — for example, CryptoPunk #5822 was worth over $23 million in 2022.
The demand for punks spurred other artists. Paintings by Beeple appeared on the market - the most expensive, Everyday’s: The First 5000 Days, was sold for $69 million. In 2021, the developer of the Nyan Cat game, Chris Torres, released an NFT dedicated to it and sold it for $590 thousand. Regular users, less-known artists, and designers also created and sold their tokens.
In 2021, the market volume of non-fungible tokens reached $16 billion. Then the cryptocurrency market entered a crypto winter: Bitcoin fell in price and dragged other coins down with it, investors got scared, trading volumes began to decline, and there were fewer new developments. The trend partially affected NFTs: it may have seemed that the trend for non-fungible tokens had completely disappeared. But in fact, it just transformed: the market leveled off, the strong bias towards collecting disappeared, and resources were redistributed among art, blockchain games, and metaverses.

Platforms for Working with NFTs
Users can interact with NFTs through special platforms where they can create, buy, and sell non-fungible tokens.
OpenSea
OpenSea is one of the largest and most popular NFT trading platforms, also one of the first (created in 2017). A classic marketplace that supports Ethereum, Polygon, Klaytn, and Solana blockchains. It only works with Ethereum standard tokens: ERC-20 for payment and ERC721 and ERC1155 for creating collections.
Rarible
Rarible is a newer and more modest marketplace, launched in 2019. It has more limited capabilities, and trading is only possible with tokens from the internal market. The project has also implemented its own coin for internal transactions called $RARI.
Binance NFT
The cryptocurrency exchange Binance also created its own NFT platform in 2021. The platform operates on the Binance Smart Chain blockchain protocol, and in addition to auctions and token trading, it also offers staking.
Additionally, Binance hosts both official token releases from well-known projects and verified authors and unofficial releases with works by lesser-known artists.
What Can Be Turned into NFTs
NFT development is possible in various sectors. You can tokenize:
- Works of visual art - both created in digital format and scanned from paper, such as illustrations, paintings, drawings, or even images generated by artificial intelligence.
- Photographs - of any meaning and content, taken with a camera or phone.
- Music and audio - these can be music tracks, albums, sound effects, or entire compositions.
- Videos - video clips, 2D and 3D animations, GIF files, or video art.
- Gaming items in games where there is a user-generated content function - accessories, skins, weapons.
- Items for metaverses - from collectible items such as trading cards, toys, figurines (in fact, all the same graphical content), to virtual real estate.
- Clothing - this practice is followed by global brands and fashion houses. Collections have been released by Adidas, Gucci, Nike, Dolce&Gabbana, and other well-known companies.
- Educational materials - these can also be tokenized and distributed using non-fungible tokens. For example, courses, educational materials, or books.
- Certificates, access rights to online events, goods or services, the right to vote for updates in the project, and even tickets for use in real-world establishments - theaters, concerts, or cinemas (which eliminates the problem of fraud) can also be tokenized.
How to Create NFTs Yourself
Developing your own NFTs doesn't always require the help of programmers and designers - you can limit yourself to the services of the marketplaces mentioned above. You will need something you want to turn into an NFT — for example, an image — and a cryptocurrency wallet that supports ERC-20 token standards. You need to top up the deposit in advance - most services charge a fee for creating tokens. You can buy cryptocurrency on an exchange or through an exchanger.
Next, to develop the NFT itself, you need to register on one of the marketplaces. The algorithm of actions on them is similar:
- Link your wallet to the marketplace. Gas fees will be charged from it when minting new tokens.
- Upload content to the platform. You can simply drag and drop the file - most platforms support various formats. For example, for OpenSea, these are PNG, JPG, GIF, SVG, MP3, and others up to 100 MB in size.
- Describe the future token. Enter the name, description, if necessary, attach a link to external sources - for example, your blog or portfolio.
- Choose a blockchain if your marketplace supports multiple options. After that, just press a button - and the service will automatically generate a new NFT without your participation. After token generation, it will be stored in the blockchain, tied to your wallet.
You can keep the token for yourself, or you can sell it where you created it - to do this, you need to list it. OpenSea offers authors two formats for selling tokens: at a fixed price or through an auction.
After developing and listing the NFT, all you have to do is wait for a buyer. It is worth noting that even now, on the marketplace, there is fierce competition and many authors - including lesser-known ones. Therefore, sometimes tokens are not sold as quickly as their creator would like, or they are not sold at all.
Custom NFT Development
If the task is to develop a commercial and large collection, in this case, the creation of tokens is delegated to specialists. Here are a few examples of using NFTs for business:
- Organizing advertising campaigns
- Releasing limited editions for regular or premium customers
- Entering new markets
- Drawing attention to new products or services of the company
Gucci, which we have already mentioned in this article, created their own tokens and even held entire fashion shows in metaverses. Thus, the fashion house supported the trend, made another statement about itself, found a new audience, and gained an additional source of income.
Naturally, such collections are not developed on the fly - a team of performers is hired to prepare them, who have already worked with blockchain. Designers (or artists, or animators, depending on the characteristics of the future token) are primarily responsible for development - they create the basis that needs to be tokenized. If the token has a different format, audio, video - composers, videographers, animators involved in the creative part are accordingly brought into the process.
Next, an NFT developer takes over. Unlike cases of private use, where a marketplace is used to create a token, developers of large commercial projects work with the blockchain manually.
In addition to the people who create the token, community specialists and marketers are also involved in the development. They have their task: to talk about the project, come up with its uniqueness for the market, attract the audience's attention, and stand out among competitors.
The development of a collection can take time - depending on its size and complexity. Usually, it takes at least several months.

Conclusion
Non-fungible tokens started as ordinary tokenized images, primarily of interest to collectors. Over the years, they have transformed into a powerful marketing and promotion tool for businesses and a way to make money for private users.
In the best traditions of the blockchain industry, the technology is accessible to everyone - you can engage in token development even without special knowledge and skills, and a team of developers is only needed for large commercial projects.